- Home
-
-
-
Stiles Enhancement Technologies
-
-
-
-
- Stiles can introduce you to advances in software integration. From raw materials to design, from production to shipping, our solutions help you manage your manufacturing processes by delivering more powerful information and greater control.
- Integration
- Data Development
- Training
- Maintenance & Support
-
-
-
- Stiles Machinery hosts a national network of five regional service centers and nationwide force of over 200 Field Service Representatives put the industry’s best service where it belongs – close to you.
- Routine & Preventative Maintenance
- Technical Support & Diagnostics
- Field Service
- Request an Equipment Manual
-
For support and service of your machinery, Stiles has experts available 24/7 to help reduce downtime and get you back in action.
Technical Support: 616-698-6615
Service & Repairs: 616-698-7500
24/7 Parts: 1-800-727-8780
sale@inlandmachineokc.com
-
-
Parts are available from Stiles 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and are shipped from our Grand Rapids, Michigan fulfillment center.
24/7 Parts: 800-727-8780
-
-

With a customized Stiles University course, we can provide expert training for your team, on-location. Whether it's programming, operation or maintenance, we want to help you train your personnel to meet your production goals efficiently and effectively.
-

Experience the trusted workforce development training and machinery knowledge you rely on from Stiles University, now at your convenience. With technology changing every day and new methods being developed constantly, Stiles University Online has the latest information and training content available at your fingertips.
-
Your solution for workforce development.
616-698-7500
-
-
-

Do you want to produce more efficiently? Processes and flows are key. We optimize these together with you, re-organize them and make sure that you reduce your lead time and save costs. This enables you to implement customized manufacturing and achieve your business goals.
-

Industrialized construction is evolving. Automation, robotics and advanced technology are raising the level of productivity, efficiency and precision for builders in North America.
-

Stiles Machinery is at the forefront of providing technology and machining for producing high quality mass timber. Automated solutions for your mass timber production can increase your manufacturing quality and productivity.
-

Project management services from Stiles make it easy to streamline your entire project— from concept and consultation to integration and implementation.
-
- Online Store
- News
- Careers
- REQUEST INFO
- Home
-
-
-
Stiles Enhancement Technologies
-
-
-
-
- Stiles can introduce you to advances in software integration. From raw materials to design, from production to shipping, our solutions help you manage your manufacturing processes by delivering more powerful information and greater control.
- Integration
- Data Development
- Training
- Maintenance & Support
-
-
-
- Stiles Machinery hosts a national network of five regional service centers and nationwide force of over 200 Field Service Representatives put the industry’s best service where it belongs – close to you.
- Routine & Preventative Maintenance
- Technical Support & Diagnostics
- Field Service
- Request an Equipment Manual
-
For support and service of your machinery, Stiles has experts available 24/7 to help reduce downtime and get you back in action.
Technical Support: 616-698-6615
Service & Repairs: 616-698-7500
24/7 Parts: 1-800-727-8780
sale@inlandmachineokc.com
-
-
Parts are available from Stiles 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and are shipped from our Grand Rapids, Michigan fulfillment center.
24/7 Parts: 800-727-8780
-
-

With a customized Stiles University course, we can provide expert training for your team, on-location. Whether it's programming, operation or maintenance, we want to help you train your personnel to meet your production goals efficiently and effectively.
-

Experience the trusted workforce development training and machinery knowledge you rely on from Stiles University, now at your convenience. With technology changing every day and new methods being developed constantly, Stiles University Online has the latest information and training content available at your fingertips.
-
Your solution for workforce development.
616-698-7500
-
-
-

Do you want to produce more efficiently? Processes and flows are key. We optimize these together with you, re-organize them and make sure that you reduce your lead time and save costs. This enables you to implement customized manufacturing and achieve your business goals.
-

Industrialized construction is evolving. Automation, robotics and advanced technology are raising the level of productivity, efficiency and precision for builders in North America.
-

Stiles Machinery is at the forefront of providing technology and machining for producing high quality mass timber. Automated solutions for your mass timber production can increase your manufacturing quality and productivity.
-

Project management services from Stiles make it easy to streamline your entire project— from concept and consultation to integration and implementation.
-
- Online Store
- News
- Careers
- REQUEST INFO
- Home
-
-
-
- Stiles can introduce you to advances in software integration. From raw materials to design, from production to shipping, our solutions help you manage your manufacturing processes by delivering more powerful information and greater control.
- Integration
- Data Development
- Training
- Maintenance & Support
-
- TECHNICAL SUPPORT
- FIELD SERVICE
- ROUTINE & PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
- REQUEST AN EQUIPMENT MANUAL
-
For support and service of your machinery, Stiles has experts available 24/7 to help reduce downtime and get you back in action.
Technical Support: 616-698-6615 Service & Repairs: 616-698-7500 24/7 Parts: 1-800-727-8780
-
-
Parts are available from Stiles 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and are shipped from our Grand Rapids, Michigan fulfillment center.
24/7 Parts: 800-727-8780
-
- IN-PERSON TRAINING
- CUSTOMIZED COURSES & TRAINING
- STILES UNIVERSITY ONLINE
-
Your solution for workforce development.
- Online Store
- News
- Careers
- FINANCING
- Blog
- REQUEST INFO
- Home
-
-
-
- Stiles can introduce you to advances in software integration. From raw materials to design, from production to shipping, our solutions help you manage your manufacturing processes by delivering more powerful information and greater control.
- Integration
- Data Development
- Training
- Maintenance & Support
-
- TECHNICAL SUPPORT
- FIELD SERVICE
- ROUTINE & PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
- REQUEST AN EQUIPMENT MANUAL
-
For support and service of your machinery, Stiles has experts available 24/7 to help reduce downtime and get you back in action.
Technical Support: 616-698-6615 Service & Repairs: 616-698-7500 24/7 Parts: 1-800-727-8780
-
-
Parts are available from Stiles 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and are shipped from our Grand Rapids, Michigan fulfillment center.
24/7 Parts: 800-727-8780
-
- IN-PERSON TRAINING
- CUSTOMIZED COURSES & TRAINING
- STILES UNIVERSITY ONLINE
-
Your solution for workforce development.
- Online Store
- News
- Careers
- FINANCING
- Blog
- REQUEST INFO
What is a Rotary Air Compressor and How Does it Work?
In today's industrial landscape, the rotary air compressor plays a pivotal role. This type of compressor uses a unique mechanism to generate compressed air efficiently. According to industry reports, rotary air compressors can increase energy efficiency by up to 15% compared to reciprocating compressors. This efficiency makes them a preferred choice for various applications, including manufacturing and HVAC systems.
However, not all rotary air compressors are created equal. Many consumers overlook maintenance needs, leading to performance issues. A well-maintained rotary air compressor can last over a decade, whereas neglect can reduce its lifespan significantly. Additionally, the market for air compressors is expected to reach $41 billion by 2026, indicating a growing reliance on these machines.
Despite their advantages, rotary air compressors require careful consideration. Users must assess their needs, as not every model suits every task. Understanding specifications is crucial to avoid common pitfalls. Investing in the right rotary air compressor can ensure productivity and cost-effectiveness in various operations.

What is a Rotary Air Compressor?
A rotary air compressor is a mechanical device used to compress air. It operates using a rotating mechanism, which efficiently compresses air to increase its pressure. This type of compressor is known for its continuous operation and efficiency, making it popular in various industries. With fewer moving parts, it typically requires less maintenance than other types of compressors.
Inside a rotary air compressor, two rotors turn in opposite directions. As they rotate, air is drawn into the chamber and compressed. The design allows for smooth and constant airflow. However, the heat generated during compression can affect efficiency. Proper cooling is crucial for optimal performance. Sometimes, users overlook the importance of airflow management, leading to inefficiencies.
One challenge with rotary air compressors is noise. They can be louder than expected, which may require additional soundproofing measures. Additionally, their upfront cost can be higher compared to simpler compressors. It's important to weigh these factors against long-term benefits. Users must reflect on their specific needs to determine if a rotary air compressor is the right choice.
Types of Rotary Air Compressors
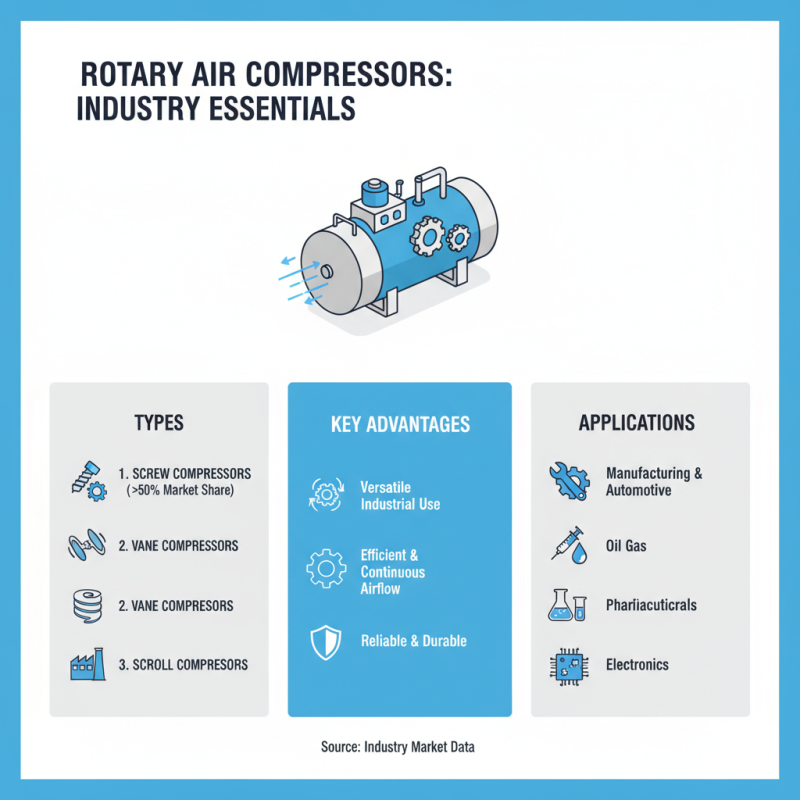
Rotary air compressors are essential in various industries. They come in different types, each suited for specific applications. The main types are screw compressors, vane compressors, and scroll compressors. Screw compressors dominate the market, accounting for over 50% of rotary compressor sales, according to industry data.
Screw compressors utilize two interlocking helical rotors. This design provides continuous air flow, making them efficient for high-demand applications. Vane compressors offer simpler designs, using sliding vanes to trap air. They are often employed in lighter industrial environments but may lack the power of screw types.
Tips: When choosing a rotary air compressor, consider the required air pressure and flow rate. It’s essential to match your compressor to the specific needs of your operation. Also, pay attention to the efficiency ratings of various designs. They can influence operational costs significantly.
Scroll compressors, while less common, are valued for their compactness and low noise levels. They work by enclosing two spiral-shaped scrolls. These compressors shine in smaller applications where quiet operation is crucial. However, they may not be optimal for high volume needs.
Be aware of the trade-offs. Each type has its benefits and limitations. Understanding these can help you make a better decision for your air compression needs.
How Rotary Air Compressors Work
Rotary air compressors are popular in various industries due to their efficiency and reliability. They operate through a simple yet effective mechanism. Two rotors rotate in opposite directions within a casing. As they turn, they trap air and reduce its volume, resulting in compressed air. This method minimizes energy loss, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. According to a report from the International Compressor Engineering Conference, rotary compressors can achieve energy efficiencies exceeding 90%.
The design plays a crucial role in performance. The rotors are precisely engineered for minimal tolerance, which greatly improves air compression. The process generates continuous airflow, unlike other types. Studies indicate that these compressors can sustain long operations without significant downtime. However, maintenance requirements can affect reliability. Simple issues often lead to costly repairs if overlooked.
Another critical factor is noise. Rotary compressors can be loud, reaching levels of 80-90 dB. This could be an issue in a quiet working environment. Solutions include soundproofing enclosures, which can be expensive to implement. The balance between cost, efficiency, and noise must be carefully considered by businesses.
Applications of Rotary Air Compressors
Rotary air compressors are essential in various industrial applications. They provide a steady flow of compressed air, which powers tools, equipment, and processes. Commonly used in manufacturing, construction, and food processing, these compressors have gained popularity due to their efficiency and reliability.
In the automotive industry, rotary air compressors are used for spray painting and tire inflation. A report noted that over 40% of automotive services depend on compressed air. In food and beverage production, these compressors help in packaging and processing. This ensures that products remain fresh and contamination-free.
Tip: Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. Inspect and replace filters often. This prevents dust build-up, which can lead to inefficient operation.
In applications like textiles and pharmaceuticals, rotary compressors play a pivotal role. They maintain precise pressure levels, which is vital in these sectors. A study found that a 10% increase in efficiency can save hundreds of dollars annually. However, choosing the right compressor for your needs requires careful consideration. It’s important to analyze your specific requirements and evaluate energy consumption.
Tip: Work with professionals to determine the right size and model for your operations. This can avoid costly mistakes down the line.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rotary Air Compressors
Rotary air compressors are popular in various industries. They offer several advantages. These compressors have a continuous operation feature. This allows them to deliver a steady supply of compressed air. They also tend to be more efficient than other types. Their design minimizes energy costs. Often, they require less maintenance than piston compressors. This makes them appealing for many users.
However, there are downsides to consider. Rotary air compressors can be quite expensive upfront. Their initial cost might deter small businesses. Noise is another factor. While quieter than some alternatives, they can still generate substantial sound levels. This could be an issue in noise-sensitive environments. Additionally, their complexity may lead to higher repair costs over time. Users should weigh these factors carefully. The decision to invest should be based on specific needs. Balancing efficiency and cost is not always easy.
What is a Rotary Air Compressor and How Does it Work? - Advantages and Disadvantages of Rotary Air Compressors
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Positive displacement compressor |
| Operation Principle | Uses rotating elements to compress air |
| Common Applications | Industrial facilities, automotive shops, construction sites |
| Advantages | High efficiency, continuous operation, low noise levels |
| Disadvantages | Higher initial cost, more complex maintenance |
| Capacity Range | From 5 HP to over 100 HP |
| Typical Pressure Range | 60 to 150 psi |
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using a Wood CNC Machine for Your Projects?
-

What is a Woodworking CNC Machine and How Does it Work?
-

Top 10 Tips for Using a Sliding Table Saw Efficiently and Safely
-

Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Rotary Screw Compressor for Your Needs
-

2026 Top Woodworking CNC Machines: Features, Benefits, and Buying Guide
-

Top 5 CNC Router Kits for Ultimate Precision and DIY Projects in 2023